Table Of Content
These measures may be invasive or non-invasive, and may be administered in a laboratory or clinical setting. Blinding involves keeping participants, researchers, or both unaware of which treatment group participants are in, in order to reduce the risk of bias in the results. Laboratory experiments are conducted under controlled conditions, which allows for greater precision and accuracy. However, because laboratory conditions are not always representative of real-world conditions, the results of these experiments may not be generalizable to the population at large. The important thing here is that when we start to evaluate the result, we will obtain very valuable information about the direction in which to move for improving the result. We will understand that we should reposition the experimental plan according to the dashed arrow.
A Quick Guide to Experimental Design 5 Steps & Examples
Below is an example of a table that shows the yield that was obtained when changing the volume from 500 to 700 ml. In the scatterplot on the right, we have plotted the measured yield against the change in reaction volume, and it doesn’t take long to see that the best volume is located at 550 ml. So, for example, first we might fix the pH at 3, and change the volume of the reaction container from a low setting of 500ml to a high of 700ml. In order to understand why Design of Experiments is so valuable, it may be helpful to take a look at what DOE helps you achieve. A good way to illustrate this is by looking at an alternative approach, one that we call the “COST” approach. It’s also helpful to see an example of the kinds of Factors that are in an Experiment.
Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
Probably many factors, temperature and moisture, various ratios of ingredients, and presence or absence of many additives. Now, should one keep all the factors involved in the experiment at a constant level and just vary one to see what would happen? This is one of the concepts that we will address in this course. Then measure your chosen response variable at several (at least two) settings of the factor under study. If changing the factor causes the phenomenon to change, then you conclude that there is indeed a cause-and-effect relationship at work. Run all possible combinations of factor levels, in random order to average out effects of lurking variables.
The Little Albert Experiment - Verywell Mind
The Little Albert Experiment.
Posted: Fri, 02 Dec 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Types of Experimental Designs
In a factorial design, participants are randomly assigned to one of several groups, each of which receives a different combination of two or more independent variables. This paper presents the application of an advanced quality management tool, the design of experiments (DOE), in order to characterise a new material (carbon fibre-reinforced polyamide) used in the 3D printing process. The study focuses on the definition of optimal 3D printing parameters, such as nozzle size, temperature, print speed, layer height and print orientation, to achieve desired mechanical properties. The results show that layer height and print orientation have a significant effect on mechanical properties and printing time.
Overview: What is DOE?
Video recording involves recording participants’ behavior or interactions using cameras or other recording equipment. This method can be used to capture detailed information about participants’ behavior or to analyze social interactions. Behavioral measures involve measuring participants’ behavior directly, such as through reaction time tasks or performance tests.
Want to Pass Your Six Sigma Exam the First Time through?
Factors might include preheating the oven, baking time, ingredients, amount of moisture, baking temperature, etc.-- what else? You probably follow a recipe so there are many additional factors that control the ingredients - i.e., a mixture. What parts of the recipe did they vary to make the recipe a success?
The control group tells us what would have happened to your test subjects without any experimental intervention. First, you may need to decide how widely to vary your independent variable. Start by simply listing the independent and dependent variables. As well as these savings, DOE achieves higher precision and reduced variability when estimating the effects of each factor or interaction than using OFAT. It also systematically estimates the interaction between factors, which is not possible with OFAT experiments. Design of experiments allows you to test numerous factors to determine which make the largest contributions to yield and taste.
A full factorial design provides information about all the possible interactions. Fractional factorial designs will provide limited interaction information because you did not test all the possible combinations. But, what if you aren’t able to run the entire set of combinations of a full factorial? What if you have monetary or time constraints, or too many variables? This is when you might choose to run a fractional factorial, also referred to as a screening DOE, which uses only a fraction of the total runs. That fraction can be one-half, one-quarter, one-eighth, and so forth depending on the number of factors or variables.
Types of Experimental Design
In this design, the experimental units are classified into subgroups of similar categories. The blocks are classified in such a way in the variability within each block should be less than the variability among the blocks. This block design is quite efficient as it reduces the variability and produces a better estimation. Regression analysis is used to model the relationship between two or more variables in order to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
The technique allows you to simultaneously control and manipulate multiple input factors to determine their effect on a desired output or response. By simultaneously testing multiple inputs, your DOE can identify significant interactions you might miss if you were only testing one factor at a time. The main effects of a DOE are the individual factors that have a statistically significant effect on your output. In the common two-level DOE, an effect is measured by subtracting the response value for running at the high level from the response value for running at the low level.
However, the focus of the course is on the design and not on the analysis. Please include what you were doing when this page came up and the Cloudflare Ray ID found at the bottom of this page.
An experimental design where treatments aren’t randomly assigned is called a quasi-experimental design. You can either use full factorial designs with all possible factor combinations, or fractional factorial designs using smaller subsets of the combinations. The use of a control group is an important experimental design method that involves having a group of participants that do not receive the treatment or intervention being studied. The control group is used as a baseline to compare the effects of the treatment group.
For example, we can estimate what we call a linear model, or an interaction model, or a quadratic model. So the selected experimental plan will support a specific type of model. If we take the approach of using three factors, the experimental protocol will start to define a cube rather than a rectangle. These four points can be optimally supplemented by a couple of points representing the variation in the interior part of the experimental design.
Full Factorial Design is a thorough and exhaustive way of determining how each factor or combination of factors affects the outcome of an experiment—at least one trial for all possible combinations of factors and levels. A confounding variable is related to both the supposed cause and the supposed effect of the study. It can be difficult to separate the true effect of the independent variable from the effect of the confounding variable. Finally, you need to decide how you’ll collect data on your dependent variable outcomes. You should aim for reliable and valid measurements that minimise bias or error.
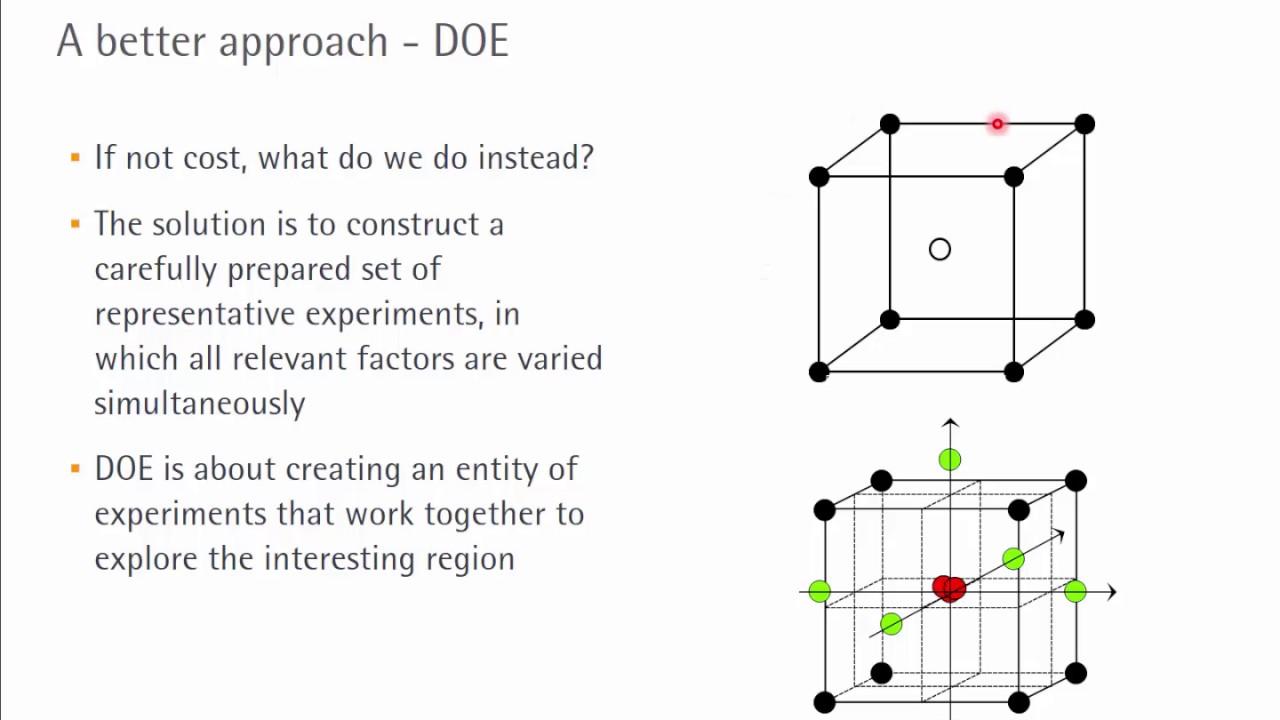
Project Managers who excel in planning will be able to apply that skill to the running of a Design of Experiments for their project. Specific tasks must be conducted in a certain sequence to achieve statistically relevant results. We can see three main reasons that DOE Is a better approach to experiment design than the COST approach. In this way, DOE allows you to construct a carefully prepared set of representative experiments, in which all relevant factors are varied simultaneously. The optimal combination for the best yield would be a volume of 550 ml and pH 4.5.

No comments:
Post a Comment